by Naomi L. | October 4, 2017 | Blog, Creative Writing |
It’s the first week of October, so regular readers of mine, you know the drill: it’s time to dive once again into my all-time favorite story, Romeo & Juliet! In the past, I’ve covered five points in the story that are often missed, the reasons it really is a great love story, a review of the book with both the play and the musical adaptation, and five lessons about love that can be learned from this story. Now I’m ready to cover even more of this timeless classic!
This year, I decided to dig a little deeper into the story and dedicate my annual R&J post to the literary devices that uphold it. So on that note, here are five major themes and motifs in Shakespeare’s Romeo & Juliet. Enjoy!
1) The Power of Love
But my true love is grown to such excess / I cannot sum up sum of half my wealth. – Juliet Capulet (2.6.33–34)
This one is kind of a given, but it’s such a prominent theme in Romeo & Juliet that it forever warrants a place at the top of the list. Though debates reign about the extent of the roles of fate, hatred, and violence in the play, it’s obvious that love is by far the most powerful force in this story. It brings the young lovers together, motivates them to risk everything to be together, and drives them to their tragic end. So let’s explore how powerful love really is in Romeo & Juliet, shall we?
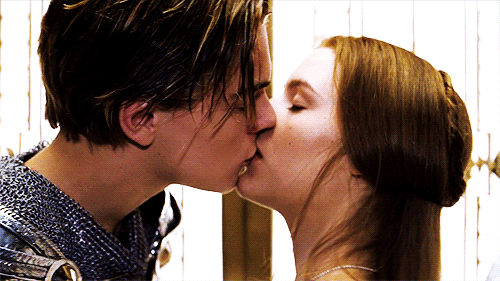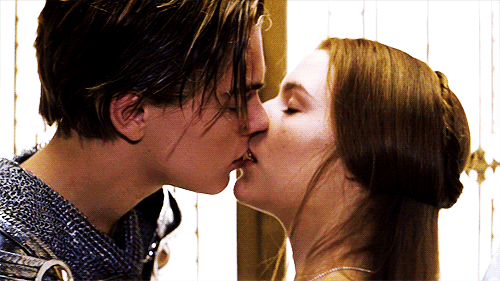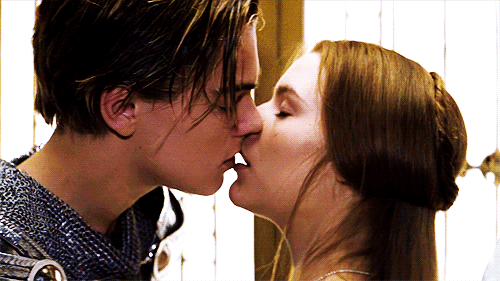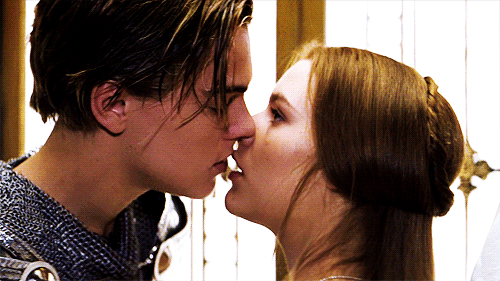
“Then have my lips the sin that they have took.” (1.5.110)
Romeo and Juliet share their first kiss (Romeo + Juliet, 1996)
To start, it’s important to define the type of love that dominates the play. There’s no question that the love in Romeo & Juliet is romantic, but what often gets overlooked is the fact that it’s also amoral. While other poets before him romanticized love as a beautiful and pure emotion, Shakespeare was more interested in portraying it as an intense and violent force that drives people into chaos and overpowers all other priorities, including life itself.

“You kiss by th’ book.” (1.5.112)
Romeo and Juliet find a moment of privacy at the Capulet Ball (Romeo & Juliet, 2013)
The greatest evidence of love’s intensity in Romeo & Juliet is the wide variety of descriptions and metaphors it receives throughout the play. In the sonnet that makes up Romeo and Juliet’s first conversation, love is described in religious terms, while in the prologue of Act II, the feeling is equated to magic. Its dangers are also mentioned by other characters: Friar Laurence warns Romeo about the fickleness of young love, while Mercutio’s Queen Mab speech outright criticizes the delusions of lovers’ dreams. Juliet even loves Romeo so much that she hardly has enough words to express her feelings all at once. Every character in the play seems to have an opinion on love, yet not one of them manages to describe it completely. It seems love, at least according to Shakespeare, is so powerful that it can’t be contained in any one definition.
Though the love in Romeo & Juliet is romantic, it’s far from idealized. Unlike the cheesy version in the bad poetry Romeo recites about Rosaline, Shakespeare’s depiction of love is a far more passionate and chaotic emotion that can evoke an astonishing amount of beauty and tragedy in a short period of time. No wonder this story is still so popular today; every time I read it, there’s something new to learn about love!
2) The Inevitability of Fate
A greater power than we can contradict / Hath thwarted our intents. – Friar Laurence (5.3.153–54)

The star-crossed lovers meet their untimely end (Romeo + Juliet, 1996)
If love is the strongest theme in Romeo & Juliet, fate is a close second. From the opening lines of the chorus, it’s made clear to the audience that the young lovers are pretty much doomed from the start. While there is a solid argument that society is really to blame for Romeo and Juliet’s deaths, the fact that Shakespeare peppered his play with references to fate, fortune, and the stars hints at the idea that every circumstance leading up to the main characters’ tragic end was always out of their control.
Notably, the role of fate in this story isn’t just clear to the audience; it’s also evident to the characters themselves. Through the second half of the play, after Mercutio and Tybalt are killed, death always seems to linger in the corner of the lovers’ minds. They’re both haunted by omens—such as each other’s pale faces after spending the night together or Juliet’s vision of Tybalt’s ghost before taking the sleeping potion—and though they try to stave off the looming threat of tragedy, it soon becomes clear that their story can only end in their untimely deaths.
The inevitability of fate is emphasized by the many forms it takes throughout the play:
- The feud between the Capulets and Montagues, which is purposely never explained
- References to fate by the characters – “O, I am fortune’s fool!” (3.1.141), “Then I defy you, stars.” (5.1.24)
- Friar Laurence’s letter failing to reach Romeo
- Romeo dying just before Juliet wakes up
While fate often seems like an external and impersonal divine force driving the characters’ lives, it also manifests as the direct forces influencing Romeo and Juliet’s choices. The rivalry between the noble households culminates in the double murder that complicates the lovers’ marriage, and Capulet’s decision to change the day of the wedding contributes to the rush of events that leads to the final tragedy. Even the protagonists themselves play directly into the hands of fate. The irony of Romeo’s decision to die alongside Juliet is that by trying to defy fate, he inadvertently brings it about: Juliet kills herself as soon as she finds him dead, thus completing the tragic sequence of events set in motion from the play’s very first scene.

Juliet stabs herself with Romeo’s dagger and dies by his side (Romeo and Juliet, 1968)
Much like love, fate in Romeo & Juliet is an amoral and overpowering force that none of the characters can resist. Despite all their efforts to love each other in peace, Romeo and Juliet can never escape their tragic destiny as the “pair of star-crossed lovers” who “take their life”, immortalizing them as the ill-fated couple of one of the greatest love stories ever told.
3) The Duality of Passion (Love and Violence)
If the entire story of Romeo & Juliet could be summed up in one word, that word would be passion. Almost every scene in the play involves characters succumbing to powerful emotions that drive their actions and, consequently, the plot. Observe:
-

“My bounty is as boundless as the sea, / My love as deep; the more I give to thee, / The more I have, for both are infinite.” (2.2.133–35)
Act I: Montague and Capulet servants fight each other in the street (establishing the long-standing feud), Romeo agrees to attend the Capulet ball for the chance to see a girl he thinks he loves, Romeo and Juliet meet and fall in love at first sight
- Act II: Romeo risks death by trespassing into the Capulet orchard to see Juliet again, Romeo and Juliet declare their love for each other, Romeo proposes to Juliet the next day (via the Nurse), Romeo and Juliet get married
- Act III: Tybalt challenges Romeo to a duel for crashing the Capulet ball, Mercutio fights Tybalt to defend Romeo’s honor, Tybalt kills Mercutio, Romeo fights and kills Tybalt to avenge Mercutio, Romeo almost kills himself out of guilt, Romeo spends the night with Juliet, Capulet threatens to disown Juliet if she doesn’t marry Paris in two days
- Act IV: Juliet threatens to kill herself if Friar Laurence can’t help her get out of marrying Paris, Capulet gets so excited about Juliet becoming obedient that he moves the wedding up to tomorrow, Juliet drinks the sleeping potion Friar Laurence gives her to fake her death
- Act V: Romeo buys poison to kill himself after hearing that Juliet has died, Paris blocks Romeo from entering the Capulet tomb upon assuming he’s there to vandalize Juliet and Tybalt’s bodies, Romeo kills Paris outside the Capulet tomb, Romeo drinks the poison and dies beside Juliet, Juliet wakes up and stabs herself with Romeo’s dagger, Montague and Capulet reconcile over their children’s deaths
Notice how virtually every important action in this play is caused by some intense emotion, whether it’s overpowering love or violent hatred. What’s especially intriguing about the passion in Romeo & Juliet is that love and violence, however polar they may seem, are constantly intertwined. Indeed, the shadow of death hangs over the play’s characters from the prologue to the final scene, and it always manifests as a consequence of passion, as much in love as in hate.

“Ha, banishment? Be merciful, say death.” (3.3.12)
The connection between love and violence in Romeo & Juliet is most evident in the actions and thoughts of the lovers themselves. Both Romeo and Juliet threaten to kill themselves at the first obstacle to their love, each one imagines the other looking dead the morning after their wedding night, and their intensely passionate “star-crossed love” culminates in their double suicide. While their goal is always to keep their love pure, the fact that they both resort to violence to achieve that end supports the story’s major theme of passion as a powerful and blinding force that few can resist.
By all accounts, passion seems to be the cause of all the conflict and grief in Romeo & Juliet. Then again, without passion, there would be no story in the first place, would there?
4) Light and Darkness
More light and light, more dark and dark our woes. – Romeo Montague (3.5.36)

“Gallop apace, you fiery-footed steeds” (3.2.1)
A particularly prominent motif in Romeo & Juliet is the imagery of light and darkness. This motif manifests most frequently in night and day, as much of the action in the play happens either at night or in the morning. And while it doesn’t necessarily highlight any moral statement, the light and dark imagery of Romeo & Juliet does provide an interesting contrast throughout the story.
The most famous example of this imagery is during the balcony scene when Romeo describes Juliet as the sun, being so beautiful and radiant that she has the power to turn night into day. Another well-known example of this contrast is the morning after their wedding night, when the lovers playfully argue about the time of day before Romeo leaves for Mantua. These scenes highlight differing perspectives of the world and emphasize how Romeo and Juliet seek refuge in their love to oppose the reality that threatens to separate them.

“Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day.” (3.5.1)
Unlike many other stories that use this motif to symbolize good and evil, the light and darkness in Romeo & Juliet are far more neutral. The lovers favor darkness because it gives them the privacy they desire, yet they see only light in each other. And although it never plays a direct role in their story, the contrast of light and dark does permeate the play until it culminates in a final poetic union: the darkness of Romeo and Juliet’s deaths and the light of hope in their families’ reconciliation.
5) Individuality vs. Social Conformity

“Alla stoccata carries it away.” (3.1.77)
While love and fate pull most of the strings in Romeo & Juliet, the lives of the main characters are further complicated by the obstacles imposed by their society. Throughout the story, Romeo and Juliet struggle (with varying degrees of success) to defy the social institutions that oppose their love, such as:
- Family and patriarchy
- Religion
- Law and social order
- Masculine honor
Yet despite the challenges they face, the young lovers repeatedly prove that their love is stronger than the social norms that threaten to keep them apart. Juliet defies her father’s authority in order to marry the man she loves and remain loyal to him to the end. Romeo compares Juliet to the sun and considers her more beautiful than the goddess of the moon, while Juliet refers to Romeo as the “god of my idolatry” (2.2.114). While still banished, Romeo returns to Verona to see Juliet one last time before he dies. Romeo refuses Tybalt’s challenge for Juliet’s sake (though he later succumbs to the pressure of honor after Mercutio is killed).
By constantly rebelling against their world, Romeo and Juliet establish themselves as individuals who seek to distance themselves from the obligations their public social lives impose upon them. Yet despite their best efforts to rebel through individuality, these social institutions continue to force them further into a corner until they’re left with only one option for escape. If anything, the greatest tragedy of Romeo & Juliet is that as powerful and beautiful as their love is, they can only find peace from their poisonous society through the ultimate form of darkness and privacy: an eternity together in death.
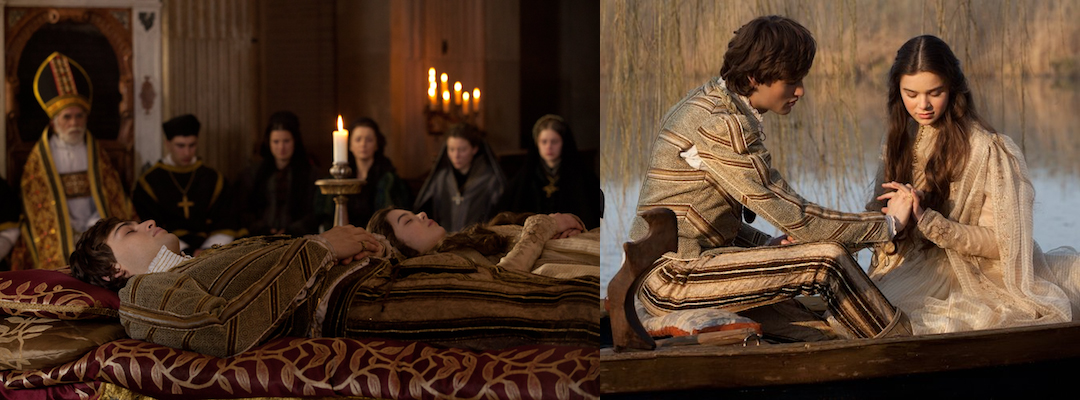

“For never was a story of more woe, / Than this of Juliet and her Romeo.” (5.3.309–10)
What are your thoughts on these themes and motifs in Romeo & Juliet? Any other interesting themes you would add to this list?
by Naomi L. | September 20, 2017 | Blog, Creative Writing, Off The Bookshelf |
Last year, I reached my first-ever Goodreads Reading Challenge goal of ten books, most of which were historical fiction. I’ve already covered Pride and Prejudice and Sense and Sensibility by Jane Austen in my Off the Bookshelf segment, so today I’m switching over to another author whose novel I really enjoyed: The Picture of Dorian Gray, by Oscar Wilde!

The Picture of Dorian Gray, by Oscar Wilde
Summary
The Picture of Dorian Gray is the only novel written by Irish poet and playwright Oscar Wilde. First published in Lippincott’s Monthly Magazine in July 1890, the novel exists in three versions: the censored 13-chapter edition published in the magazine in 1890, the revised 20-chapter book edition published in 1891, and the uncensored 13-chapter edition submitted to the magazine with all of Wilde’s original material intact. The story follows the moral corruption and downfall of Dorian Gray, a handsome yet narcissistic young man whose vanity leads him to wish that a painting of himself will age in his stead. After his wish comes true, Dorian succumbs to a hedonistic lifestyle of vice and sin from which his insatiable desire for pleasure leaves him little chance to escape.
Review
If it were only the other way! If it were I who was to be always young, and the picture that was to grow old! For that—for that—I would give everything! Yes, there is nothing in the whole world I would not give! I would give my soul for that! – Dorian Gray
A brief disclaimer: Because Wilde’s novel exists in three different forms, each one differs slightly from the others, in some cases affecting the plot. The version I read is the 1891 20-chapter book, so this is the edition that will be referenced throughout this review.
The Picture of Dorian Gray has often been compared to the Faust story, in which a dissatisfied scholar sells his soul to the Devil for unlimited knowledge and pleasure. Similarly, in a moment of weakness and newfound vanity, Dorian offers up his soul for the chance to remain young and handsome forever. In response to this wish, the painting becomes a mirror of Dorian’s soul and begins reflecting the effects of his actions that his body will now be spared. This inciting incident plays into the themes of valuing youth and beauty above all else and the consequences of choosing pleasure over virtue.
One of the most prominent themes in the book is the conflict between morality and pleasure. Although Dorian initially struggles with his new philosophy, his selfish desires ultimately overpower his guilt: after his romance with the young actress Sibyl Vane ends tragically, the subtle change in his portrait’s face proves his actions will have no visible consequence, as the painting will bear all the marks of his sins for him. After accepting Sibyl’s death as an artistic personification of tragedy, Dorian is free to pursue pleasure without risk and spends the next several years of his life indulging in various forms of gratification. Only in the final chapters of the story does he come to question if perpetual youth was worth the price of his soul.
Indeed, the fact that his artistic lifestyle costs him his soul is what makes Dorian Gray such an enigmatic character. Having given up his emotional depth, the protagonist’s true personality remains a mystery to the reader throughout the story. One detail of the novel that makes this evident is the heavy color motif. So many descriptions in the novel involve color in some way, and while at first I dismissed these vivid descriptions as the flowery writing of a poet, I later recognized their allusion to the main character’s internal conflict. The paradox of The Picture of Dorian Gray is that by giving up his soul for the pursuit of pleasure and the perpetuation of beauty, Dorian is no longer able to appreciate either—that is, in a world full of color and beauty, Dorian’s soulless existence is perpetually gray. Thus, Wilde’s novel—at least the revised version—supports the idea that art alone cannot bring happiness; one must have emotional depth in order to appreciate it.

From left to right: Lord Henry Wotton, Dorian Gray, Basil Hallward (Dorian Gray, 2009)
Aside from Dorian, the story features two other important characters: Basil Hallward, the painter of the infamous picture, and Lord Henry Wotton, a witty aristocrat who advocates “New Hedonism”. Both are equally fascinated by Dorian’s beauty but stand at opposite ends of his moral spectrum: Basil represents conformity to moral standards while Lord Henry represents the temptation of sin. In this way, these two gentlemen play the roles of Dorian’s “shoulder angel and devil”, respectively, and personify the novel’s overarching conflict between virtue and hedonism: Basil sees only beauty in Dorian and encourages him to remain virtuous, while Lord Henry lauds his youth and persuades him to live for pleasure above all else. And although Dorian never escapes from the guilt the painter evokes in him, the fact that the story plays out far worse for Basil than for Lord Henry further supports the novel’s theme of beauty’s superiority over virtue.
Interestingly, The Picture of Dorian Gray presents an unusual example of an unscrupulous protagonist who repeatedly dodges moral justice. While Dorian influences several people to unfortunate ends throughout his life, he himself doesn’t get what he deserves for almost the entirety of the novel. While this may be an allusion to Wilde’s aesthetic beliefs, it’s more frequently interpreted as a comment on society’s superficiality and hypocrisy; although several rumors emerge about Dorian’s immoral exploits over the years, his peers nonetheless continue to accept him because he’s beautiful and, by all appearances, innocent. Yet as with any Faustian story, sin is ultimately punished in the end, thus completing the theme of eternal pleasure coming at an exceedingly high cost.
The Picture of Dorian Gray is an intriguing novel, a mix of Gothic horror with social and artistic commentary that never seems to settle on a single form. Even the moral of the story is not so black and white as its similarity to the Faust fable would suggest, as the main character doesn’t suffer the consequences of his actions until the very end, and even then justice is brought about by his own hands. Yet by all accounts, with its enigmatic themes, poetic motifs, and structure of an unusual moral fable, Wilde has created nothing less than an outstanding and fascinating work of art.
Inspiration
There is no such thing as a moral or an immoral book. Books are well written, or badly written. That is all. – Oscar Wilde
In a strange meta twist, the most fascinating aspect of The Picture of Dorian Gray may actually be the author’s preface in the book edition. When Oscar Wilde first submitted his manuscript for publication, the editor of Lippincott’s Monthly Magazine censored the story, removing roughly 500 words without the author’s knowledge. Nevertheless, the novel was widely decried as a violation of public morality. A year later, upon publishing the revised book version, Wilde issued a preface to address these criticisms and defend his work, claiming in this artistic manifesto that the only point of art is to be beautiful, not to serve a moral purpose.

Dorian’s painting, before and after
(Image source: TV Tropes)
Yet in The Picture of Dorian Gray, the eponymous painting itself serves a moral purpose by shedding light on the high price of vanity. Despite the author’s advocacy of aestheticism, his novel suggests that art always contains some degree of meaning: though Dorian constantly tries to immerse himself in a purely artistic lifestyle, he can never escape the haunting lesson in the portrait that bares his corrupted soul. Thus, while he may not have written a truly aesthetic piece, Wilde has nonetheless created a stunning work of art that inspires a poetic theme: art and morality are perpetually intertwined.
As far as artistic inspiration, this novel certainly has its fair share of philosophy. One of the most intriguing aspects of the story is Lord Henry’s powerful influence over the naïve young Dorian. Although Lord Henry’s beliefs contrast heavily with the standards of his time, he speaks with such wit and persuasive language that one can’t help but be drawn to his ideas, however misguided they are. Indeed, the only character immune to these ideas is Basil, whose conventional mindset keeps him morally grounded but makes him utterly boring in the eyes of his impressionable muse. Reading Lord Henry’s speeches, I could easily understand how any weak-minded individual would embrace his poisonous philosophy, which thankfully is revealed to be shallow and impractical by the second half of the story. If anything, the novel is a cautionary tale about the consequences of trying to live such a hedonistic life: the pursuit of pleasure may satisfy the senses with each experience, but it still isn’t worth giving up one’s soul.
Overall, I found The Picture of Dorian Gray to be an enjoyable and intriguing read. Its themes of morality, superficiality, and artistic living make it a notable addition to literature’s vast collection of moral fables. Yet the fact that Wilde was such a strong proponent of aestheticism raises the ultimate question: if his philosophy was to create “art for art’s sake”, should we really put so much weight on the moral themes of his only novel, or take a step back to simply glimpse these undertones while admiring the beauty of his work?
by Naomi L. | May 24, 2017 | Blog, Creative Writing, Off The Bookshelf |
Back in January, I finally returned to my Off The Bookshelf segment with a review of Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice. So today, I’d like to continue my reviews by writing about the other Austen novel I read last year. Since I’ve definitely been enjoying reading her literature, there was really only one novel I could review next: Sense and Sensibility!

Sense and Sensibility, by Jane Austen
Summary
Sense and Sensibility was Austen’s debut novel, first published in London in 1811. The story follows sisters Elinor and Marianne Dashwood as they adjust to their new life with their widowed mother and younger sister, who have all been left impoverished after Mr. Dashwood’s death. Over the course of the narrative, the sisters experience love, romance, and heartbreak, and eventually come to realize that they must learn to master the delicate balance between sense and sensibility in order to achieve happiness.
Review
Though I wouldn’t say I liked it as much as Pride and Prejudice, I enjoyed Sense and Sensibility for Austen’s realistic take on romance and manners, seasoned with all her classic humor and wit. Much like in the author’s more popular novel, the main characters of this story are faced with the challenge of finding love in a world where their low income and social status put them at a severe disadvantage. What really sets this novel apart from its successor, however, is the comparison it draws between the tempers of Elinor and Marianne, who each occupy one extreme of the romance-realism spectrum.
As the title suggests, the most prominent theme in Sense and Sensibility is the contrast between good sense and overt sensitivity (known as sensibility back then). As the eldest Dashwood sister, Elinor has the best judgment in her family and is highly skilled at exercising good sense and composure. Her younger sister Marianne, on the other hand, has no control over her emotions and no desire to keep her overly sensitive demeanor in check, favoring romantic idealism over etiquette. This contrast between their personalities makes for several interesting situations throughout the story, but in the end both sisters learn the same valuable lesson: too much sense or sensibility only leads to unhappiness. Only after Elinor learns to open her heart to sensibility and Marianne learns to temper her spontaneity with sense do they both achieve their happy endings.
Another major theme in the book is the role of money and social standing in romance. Though her novels all have happy endings, Jane Austen was never one to tell an idealistic love story; in her view, even the truest love isn’t immune to the real-world obstacle of low income. In the most notable example, Marianne and Willoughby seem like a perfect match: they’re both romantic and outspoken about their opinions on art and love, and spend so much time together that everyone assumes they’re engaged before they even say a word. Unfortunately, being one of the author’s well-known “hero caricatures”, the charming Willoughby couldn’t be anything less than a scoundrel, and sure enough, his expensive tastes coupled with Marianne’s poverty lead him to jilt her for a wealthy young lady he doesn’t love. Funnily enough, the same obstacle of wealth turns out to be a saving grace for Edward Ferrars, who for most of the story finds himself honor-bound to a loveless engagement only to be saved at the end from said commitment by his disinheritance from his mother, leaving him free to give his heart to Elinor after his conniving fiancé abandons him. From beginning to end, wherever there are love and romance, the shadow of money looms in the background.
Overall, Sense and Sensibility is an enjoyable read that shows less-than-idealistic romance in a humorous light, as well as an interesting dynamic of character development between two polar opposite sisters. Just as Marianne learns from Elinor that excessive emotion can destroy one’s life, Elinor learns from Marianne that excessive repression of emotion leads to intense suffering and risk of abandonment. Still, in true Austen fashion, both sisters achieve their happy endings by the story’s conclusion, finding comfortable lives with gentlemen who can provide them with all the security and emotional fulfillment they desire. In this way, from her very first novel, the author reveals that despite all the realistic obstacles in its way, romance can still thrive in a world plagued with social barriers, a hope not yet forgotten in the modern age.
Inspiration
Much like Pride and Prejudice, Sense and Sensibility offers a glimpse into the romantic and realistic elements of past life that have survived into the present. The novel also teaches a valuable lesson on the importance of both practicing good sense and being willingly sensitive, albeit a somewhat imbalanced one that favors sense. We shouldn’t give our emotions total control over our happiness, but we also shouldn’t be afraid to feel vulnerable in the pursuit of love. There are plenty of opportunities in life to be both sensible and sensitive; it’s all a matter of exercising the right judgment.
Though her novels often highlight the limitations placed on women in the society of her day, Jane Austen clearly had a way of demonstrating the strength that women have always had to succeed within their means. Because of that, I know I can always turn to one of her novels for inspiration on writing heroines with real personalities, issues, and aspirations. Whether you seek inspiration for historical fiction, realistic characters, or contrasting themes in human behavior, Sense and Sensibility is an excellent novel that warrants a place beside Pride and Prejudice on any Austen fan’s bookshelf.
by Naomi L. | January 25, 2017 | Blog, Creative Writing, Off The Bookshelf |
Welcome back to my Off The Bookshelf segment! It’s been almost a year since I’ve written a book review for my blog, which is a shame since I do love recommending my favorite novels. The good news is that I read several new books last year and plan to read even more this year, so I’ll have plenty of material to work with in 2017!
So today, I’d like to start off this year’s reviews with my favorite novel from my 2016 list: Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen!

Pride and Prejudice, by Jane Austen
Summary
First printed in 1813, Pride and Prejudice is Jane Austen’s second published novel and one of the most beloved works in English literature. The novel follows the story of Elizabeth Bennet, an exceptionally clever young woman and the second of a country gentleman’s five daughters, as she navigates issues of manners, morality, education, and romance in the landed gentry society of the British Regency. Among her greatest challenges is dealing with Mr. Darcy, a gentleman with great wealth and even greater pride with whom she repeatedly clashes. As their relationship progresses, both Elizabeth and Mr. Darcy come to learn that first impressions are often misleading, and that they must overcome their pride and their prejudices before the story can reach its happy conclusion.
Review
Every so often, you come across a story so well written, so absolutely brilliant that it draws you in from the first sentence and keeps you hooked to the very last page. Such was my experience with Pride and Prejudice, a literary masterpiece from a brilliant mind of the turn of the 19th century. Jane Austen’s novel is still beloved by many readers today, and with good reason: it’s a comedy that covers some of humanity’s most relatable issues – love, marriage, etiquette, wealth, and morals – all from the perspective of an astute young heroine who challenges and overcomes the obstacles of her social position to achieve her happy ending.
Naturally, a central theme in Elizabeth’s story is the difference between the superficial and the indispensable, as well as the emotional development that comes with learning to distinguish the two. After all, there’s a reason the novel was originally titled First Impressions. In the beginning, the protagonist has a habit of forming her opinions of people immediately and consolidating those opinions through selective observation, a practice she believes is a credit to her intelligence. As a result, she dislikes Mr. Darcy from the day she meets him and grows to despise him the more time she spends with him, while Mr. Wickham earns her favor instantly with his charm and apparent good breeding. Halfway through the story, however, Elizabeth discovers that her preconceptions of both gentlemen were misplaced, proving that appearance isn’t always the best indicator of worth. The same lesson is learned by Mr. Darcy, who initially believes his proud behavior to be justified but is promptly put in his place by a woman he once thought was beneath him. Fortunately, both these characters prove mature enough to shed their most prominent flaws in favor of the romance that will make them “the happiest couple in the world”. First impressions are powerful, but thankfully they don’t always stick!
Another of my favorite themes of the book is the only-too-familiar contrast between proper behavior and real character. Throughout the narrative, it’s made apparent that while everyone behaves politely, some characters only do so to maintain a respectable place in high society while others are genuinely good at heart. A notable example comes up during a scene in Netherfield: when Elizabeth arrives at the Bingleys’ estate to take care of her sister Jane, who has fallen ill, all three of her hosts smile and treat her with the utmost kindness and hospitality. The second she leaves the room, however, Caroline and Louisa start criticizing Elizabeth’s dirty clothes while Charles remarks on how much she must love her sister to have walked so far on muddy roads just to see her. Even among siblings, people can vary greatly in character, but good manners are universal!
Austen was always an expert at implementing irony and satire in her writing, and Pride and Prejudice is no exception. Being witty and lively by nature, much of Elizabeth’s perspective includes hints of criticism about her reality: the influence of her family’s low income on their social standing (e.g. Jane’s failed friendship with Caroline Bingley), the excessive pride of some of her wealthier acquaintances (e.g. the unintentional insults in Mr. Darcy’s proposal), marriage as a requirement for women to secure a respectable position in society (e.g. Charlotte Lucas agreeing to marry Mr. Collins, a man she doesn’t love). And while the author didn’t necessarily discourage the following of such social rules in her novels, she did present them in a comical light that at least called these societal standards into question.
Overall, Pride and Prejudice is a fantastic novel that I would highly recommend to anyone who enjoys clever insights into human thoughts and behavior. For romantics and realists alike, this story has something for everyone and will surely continue to captivate audiences for generations, broadening our perceptions of the societal norms by which we live. To anyone who loves literature, it’s certainly an enlightening and delightfully entertaining read!
Inspiration
Ms. Austen’s beloved novel is one of those classic pieces of fiction that remains relevant long after its time. Though the story takes place in the early 19th century, its themes of social conduct, proper etiquette, and first impressions are still universal in the modern world. Whenever I need inspiration for character development, I know I can turn to an Austen novel for insight on general behavior and the restrictions of polite society to better understand how people think and function in everyday life. Basically, Pride and Prejudice is an excellent example of a point I’ve made in the past: that historical fiction can show us the elements of human nature that don’t change over time.
If you’re a historical fiction author or a writer of stories about the human condition, Pride and Prejudice will definitely be a great source of inspiration for your characters, whether they’re 19th-century country folk, 21st-century city dwellers, or anything in between. The greatest stories are those that explore what it means to be human, which makes it no surprise that this novel always appears near the top of best-books-ever-written lists. So if you haven’t yet, I strongly urge you to pick up a copy of Pride and Prejudice and see for yourself what a delightful read it truly is. You may find to your amazement that despite having lived so long ago, Jane Austen can still teach you a thing or two about the ironies of your economic and social reality!
by Naomi L. | October 7, 2015 | Blog, Creative Writing, Off The Bookshelf |
I know it’s been a while since I’ve shared a book on my Off The Bookshelf segment, so this week, I’m going to discuss one of my favorites. I’ve talked about this famous story in depth a few times before, notably to discuss five points that are often missed and the reasons why it’s a greater story than many people think. Once again, I’d like to revisit this classic tale of forbidden love, this time in a double dose. I hope you’ll enjoy this review of one of my favorite books off my shelf: Romeo & Juliet/West Side Story.

Romeo & Juliet/West Side Story
Summary
First published in 1965, Romeo & Juliet/West Side Story comprises two stories in one: the stage play Romeo & Juliet by William Shakespeare; and the 1957 Broadway musical West Side Story by Arthur Laurents. The book also includes explanatory notes for unfamiliar expressions in Shakespeare’s play and a foreword by renowned theater director Norris Houghton.
Romeo & Juliet tells the story of two teenagers in Renaissance Verona who fall in love despite the age-old feud between their families, but who are driven to an untimely end by fate and the violent circumstances surrounding them. Inspired by Shakespeare’s play, West Side Story tells the same tragic tale of a doomed romance between young lovers, but updates the setting to modern-day New York and the protagonists to a white American boy and a Puerto-Rican girl torn apart by the racism-fueled rivalry between the street gangs with which they’re associated. As much for Romeo and Juliet as for Tony and Maria, love blossoms at first sight and against the odds, only to be threatened and destroyed by hatred that brings tragedy not just to the young lovers, but to their war-torn society as a whole.
Review
 I first read this book as a teenager, shortly after watching the 1961 movie West Side Story as homework for singing lessons (I was to sing “Somewhere” at my first presentation). Long familiar with the plot of the original play, I had fallen in love with the story of forbidden romance and was eager to finally read Shakespeare’s timeless classic for myself. Of course, I’ve made my love for the story itself abundantly clear in the past, so this review will focus a little more on the format of this book than on the pieces within it.
I first read this book as a teenager, shortly after watching the 1961 movie West Side Story as homework for singing lessons (I was to sing “Somewhere” at my first presentation). Long familiar with the plot of the original play, I had fallen in love with the story of forbidden romance and was eager to finally read Shakespeare’s timeless classic for myself. Of course, I’ve made my love for the story itself abundantly clear in the past, so this review will focus a little more on the format of this book than on the pieces within it.
What I find most interesting about this particular book is the way the same story is presented over two very different backdrops: one in Renaissance Italy, the other in 1950s New York. By combining both stories into one volume, Romeo & Juliet/West Side Story offers a unique way to visualize the tale of star-crossed young love across time. The similarities and differences between these popular pieces become clearer as the reader is able to quickly swap a scene in one play for its parallel in the other: the feud between the Montagues and the Capulets becomes a turf war between the Jets and the Sharks, the Capulet ball becomes the dance at the gym, the poetic exchange at Juliet’s balcony becomes a duet on Maria’s fire escape. Each story is beautiful in its own right, but I’ve found that to be able to compare and contrast them so easily makes the fundamental plot all the more fascinating.
 Romeo & Juliet was the first Shakespearean play I ever read, so naturally I was yet unfamiliar with Elizabethan English. This is where the notes in the back of the book came in extremely handy. Essential words and terms are referenced to the line with modern English translations and explanations wherever necessary, so the notes were a tremendous help when it came to deciphering the meanings within Shakespeare’s verse. It’s worth noting that they’re still helpful to any new reader who plans to read more of Shakespeare, as several of the expressions used in Romeo & Juliet commonly appear in his other works. Unfortunately, a similar device isn’t available for West Side Story, which relies on its readers’ familiarity with the music to be fully enjoyable, but this is merely a minor drawback to what is otherwise an equally stunning theatrical masterpiece.
Romeo & Juliet was the first Shakespearean play I ever read, so naturally I was yet unfamiliar with Elizabethan English. This is where the notes in the back of the book came in extremely handy. Essential words and terms are referenced to the line with modern English translations and explanations wherever necessary, so the notes were a tremendous help when it came to deciphering the meanings within Shakespeare’s verse. It’s worth noting that they’re still helpful to any new reader who plans to read more of Shakespeare, as several of the expressions used in Romeo & Juliet commonly appear in his other works. Unfortunately, a similar device isn’t available for West Side Story, which relies on its readers’ familiarity with the music to be fully enjoyable, but this is merely a minor drawback to what is otherwise an equally stunning theatrical masterpiece.
Both Romeo & Juliet and West Side Story have had a profound impact on audiences: one for its poetic deconstruction of romantic ideals, the other for its dramatic commentary on the consequences of social intolerance. The presentation of both plays in one volume brings to light the true timelessness of Shakespeare’s classic, proving that the story of love born against hate will be forever relevant as long as people and society continue to be powerfully motivated by both.
Inspiration
Romeo & Juliet is the archetype of forbidden love thwarted by circumstance, so it’s no wonder the story has translated so well into the modern setting of West Side Story. Whether set between feuding families or warring street gangs, this tragic love story reads not only as the epitome of the passion and dangers of young romance, but as a lesson on how hatred kills. Perhaps for its universal themes of love, intolerance, and the cruelty of fate, the plight of the star-crossed lovers is a tale that has fascinated readers for centuries and certainly will for many more to come. It has served as inspiration for much of my romantic fiction, and to this day I indulge in it whenever I feel the need to satisfy my cravings for drama and romance.
For all the above reasons and more, Romeo & Juliet is and likely always will be my favorite story at its core, regardless of the characters, settings, and details that flesh it out. To be able to enjoy my two favorite versions of the story in a single volume is simply the cherry on top of a classic poetic delight.























Recent Comments